As an experienced bookkeeper, I am pleased to present this comprehensive guide on the Profit And Loss Statement. While this article provides in-depth information about P&L reports, their importance, and how to interpret them, I want to emphasize that I offer professional services to create these essential financial documents for business owners.
With my expertise in bookkeeping and financial reporting, I can:
- Prepare accurate and timely P&L statements tailored to your business needs
- Ensure compliance with relevant accounting standards and regulations
- Provide insights and explanations to help you understand your financial position
- Customize reports to highlight key performance indicators specific to your industry
- Assist in using P&L data for strategic decision-making and growth planning
As a business owner, your time is valuable, and financial reporting can be complex and time-consuming. By entrusting your P&L preparation to a professional, you can focus on what you do best – running and growing your business.
Throughout this article, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the Profit And Loss Statement and their crucial role in business management. Whether you choose to create these reports yourself or seek professional assistance, this knowledge will empower you to make informed financial decisions.
Should you decide that professional help would benefit your business, I am here to support you with expert bookkeeping services, including the creation of comprehensive and insightful P&L reports. Let’s work together to ensure your financial reporting is accurate, timely, and actionable.
Now, let’s delve into the world of profit and loss statements and discover how they can drive your business success.
Table of Contents
I. Introduction to the Profit And Loss Statement
In the complex world of business finance, few tools are as powerful and revealing as the profit and loss statement. This fundamental financial document, often overlooked or misunderstood, holds the key to unlocking your company’s true financial potential. Whether you’re a startup founder, a seasoned entrepreneur, or a curious investor, mastering the art of creating and interpreting profit and loss statements can be the difference between merely surviving and truly thriving in today’s competitive business landscape.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify profit and loss statements, exploring their intricacies and unveiling their hidden insights. You’ll learn not just how to read these crucial financial reports, but how to leverage them to make data-driven decisions that can propel your business forward. From basic concepts to advanced analysis techniques, this article will equip you with the knowledge and skills to turn your profit and loss statement into a powerful tool for financial success.
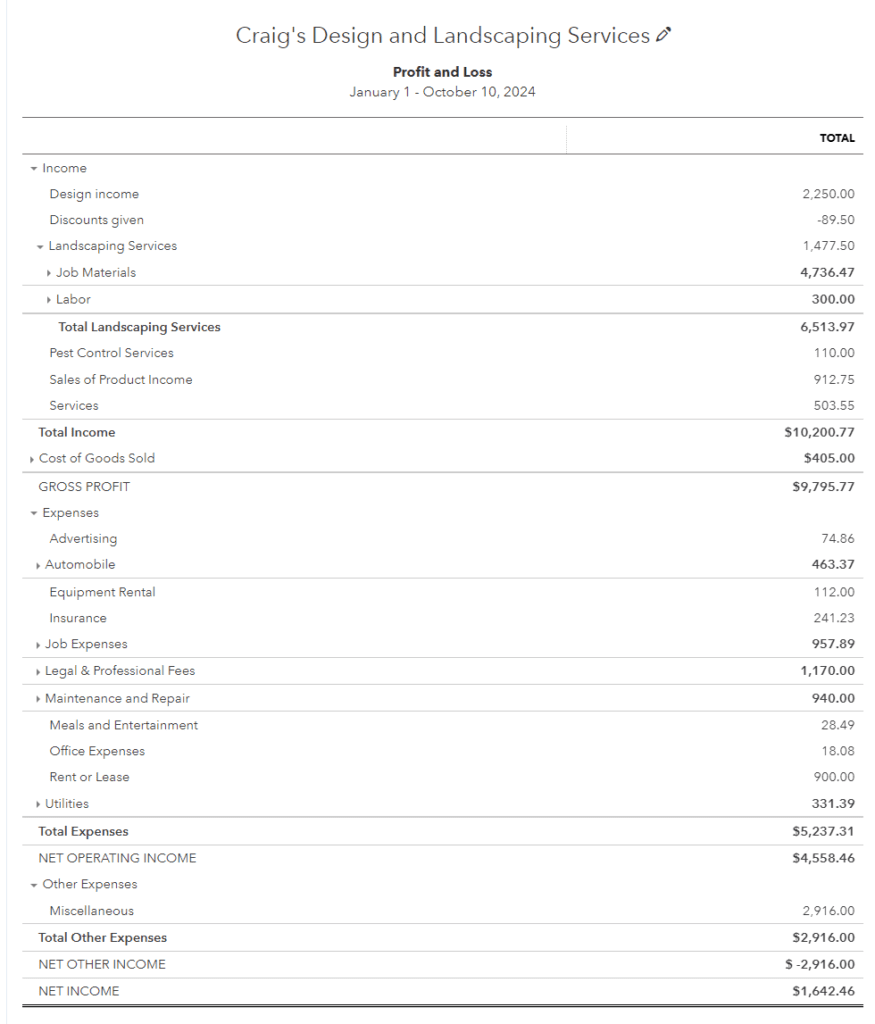
II. Understanding Profit And Loss Statement
A. Definition and Purpose
A profit and loss statement, also known as an income statement or P&L, is a financial report that summarizes a company’s revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period, typically a fiscal quarter or year. Its primary purpose is to show whether a company is generating profit or incurring a loss by subtracting all expenses from the revenue.
B. Components of a P&L Statement
- Revenue: The total amount of income generated from sales of goods or services.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold.
- Gross Profit: The difference between revenue and COGS.
- Operating Expenses: Costs incurred in the normal course of business, such as rent, utilities, and salaries.
- Operating Income: Gross profit minus operating expenses.
- Non-Operating Income and Expenses: Income or costs not directly related to core business operations.
- Net Income: The final profit or loss after all revenues and expenses have been accounted for.
C. How P&L Differs from Other Financial Statements
While the P&L statement focuses on income and expenses over time, other key financial statements serve different purposes:
- Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Cash Flow Statement: Shows how changes in balance sheet accounts and income affect cash and cash equivalents.
The P&L statement complements these documents, offering a dynamic view of a company’s financial performance that the others cannot provide alone.
III. The Crucial Role of The Profit And Loss Statement in Business
A. Assessing Financial Health
P&L statements are vital for gauging a company’s financial well-being. They reveal:
- Profitability: Whether the company is making money or losing it.
- Efficiency: How well the company manages its expenses relative to its revenue.
- Growth Trends: Changes in revenue and profitability over time.
B. Decision-Making Tool
P&L statements inform critical business decisions, such as:
- Pricing strategies: Analyzing margins to set competitive yet profitable prices.
- Cost management: Identifying areas where expenses can be reduced.
- Investment opportunities: Determining if the company can afford new initiatives or expansions.
C. Attracting Investors and Securing Loans
Investors and lenders rely heavily on P&L statements to:
- Evaluate a company’s financial stability and growth potential.
- Assess the risk associated with investing in or lending to the business.
- Compare the company’s performance to industry benchmarks.
D. Tax Reporting and Compliance
P&L statements play a crucial role in tax preparation by:
- Providing the basis for calculating taxable income.
- Helping identify tax-deductible expenses.
- Ensuring compliance with financial reporting regulations.
By understanding and effectively utilizing profit and loss statements, businesses can gain invaluable insights into their financial performance, make informed strategic decisions, and position themselves for long-term success in an ever-changing economic landscape.
IV. Creating a Comprehensive Profit And Loss Statement
A. Step-by-Step Guide
- Determine the reporting period (e.g., monthly, quarterly, or annually).
- Gather all financial data for the period.
- Calculate total revenue from all sources.
- Determine the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Calculate gross profit by subtracting COGS from revenue.
- List and sum up all operating expenses.
- Calculate operating income by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit.
- Account for non-operating income and expenses.
- Calculate net income by adding non-operating items to operating income.
- Review and verify all calculations for accuracy.
B. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Omitting or double-counting revenue or expenses.
- Misclassifying expenses (e.g., confusing COGS with operating expenses).
- Neglecting to account for non-cash expenses like depreciation.
- Inconsistent reporting periods across different financial statements.
- Failing to reconcile the P&L with other financial documents.
C. Best Practices for Accuracy and Clarity
- Use accounting software to minimize manual errors.
- Maintain detailed records of all transactions.
- Implement a consistent chart of accounts.
- Regularly reconcile bank statements with your P&L.
- Have a second person review the statement for errors.
- Use clear, descriptive labels for all line items.
- Include comparative data from previous periods.
V. Advanced Profit And Loss Statement Analysis Techniques
A. Vertical and Horizontal Analysis
- Vertical Analysis:
- Express each line item as a percentage of total revenue.
- Helps identify which expenses are taking up the largest portion of revenue.
- Horizontal Analysis:
- Compare P&L statements from different periods.
- Reveals trends and growth rates in revenue and expenses over time.
B. Ratio Analysis
- Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100
- Operating Profit Margin = (Operating Income / Revenue) x 100
- Net Profit Margin = (Net Income / Revenue) x 100
- Return on Sales (ROS) = (Operating Profit / Net Sales) x 100
These ratios provide insights into profitability and operational efficiency.
C. Trend Analysis and Forecasting
- Identify patterns in revenue and expense fluctuations.
- Use historical data to project future performance.
- Create “what-if” scenarios to anticipate potential financial outcomes.
- Adjust forecasts regularly based on actual performance and market conditions.
VI. Leveraging Technology for P&L Management
A. Overview of P&L Software Solutions
- QuickBooks: Popular for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Xero: Cloud-based accounting software with strong P&L reporting features.
- NetSuite: Comprehensive ERP system with advanced P&L capabilities.
- Sage Intacct: Financial management software with customizable P&L reports.
- FreshBooks: User-friendly option for freelancers and small businesses.
B. Integrating P&L Data with Other Business Systems
- Connect P&L software with:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems
- Inventory management tools
- Payroll systems
- E-commerce platforms
- Benefits of integration:
- Real-time financial data across all business operations
- Reduced manual data entry and associated errors
- More comprehensive and accurate financial reporting
C. Automating P&L Reporting
- Set up recurring P&L reports to generate automatically.
- Use data visualization tools to create dynamic P&L dashboards.
- Implement AI-powered analytics to identify trends and anomalies.
- Utilize cloud-based systems for real-time access to P&L data.
- Set up automated alerts for key financial metrics or variances.
By mastering these advanced techniques and leveraging modern technology, businesses can transform their P&L statements from static reports into dynamic tools for financial analysis and strategic decision-making. This approach not only saves time but also provides deeper insights into financial performance, enabling more proactive and data-driven management of business finances.
VII. Industry-Specific P&L Considerations
A. Retail
In the retail sector, profit and loss statements require special attention to several key areas:
- Inventory turnover: This metric is crucial for retailers. A high turnover rate indicates efficient inventory management, while a low rate might suggest overstocking or slow-moving products.
- Gross margin: Retailers should closely monitor gross margin percentages for different product categories to optimize pricing and product mix.
- Seasonal fluctuations: Many retailers experience significant revenue variations throughout the year. P&L statements should be analyzed with these seasonal patterns in mind.
- Sales per square foot: This metric helps evaluate the efficiency of store layouts and the effectiveness of merchandising strategies.
- Marketing expenses: Retailers often have substantial marketing budgets. The P&L should clearly show the return on investment for various marketing initiatives.
B. Manufacturing
Manufacturing businesses face unique challenges in P&L reporting and analysis:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This is typically a major expense for manufacturers. Detailed breakdown of raw materials, labor, and overhead costs is essential.
- Production efficiency: Metrics like yield rates and machine utilization should be reflected in the P&L analysis to identify areas for improvement.
- Contribution margin by product line: Understanding which products contribute most to profitability can guide production decisions and resource allocation.
- Research and Development (R&D) expenses: For many manufacturers, R&D is crucial. The P&L should clearly show these investments and their impact over time.
- Capacity utilization: This metric helps in understanding fixed cost absorption and can guide decisions on expansion or contraction.
C. Service-based Businesses
Service industries have their own set of P&L considerations:
- Revenue recognition: Service businesses often deal with complex revenue recognition issues, especially for long-term contracts or projects spanning multiple reporting periods.
- Billable hours and utilization rates: These are key performance indicators for many service businesses and should be reflected in P&L analysis.
- Employee costs: As the primary expense for most service businesses, a detailed breakdown of salaries, benefits, and training costs is crucial.
- Project profitability: Analyzing profit margins by project or client can reveal which types of work are most lucrative.
- Overhead allocation: Proper allocation of overhead costs to different service lines or projects is important for accurate profitability analysis.
D. Non-profit Organizations
Non-profits have unique P&L considerations due to their mission-driven nature:
- Program expenses vs. administrative costs: Non-profits need to demonstrate that a high percentage of funds are used for program-related activities rather than administration.
- Restricted vs. unrestricted funds: P&L statements should clearly differentiate between these two types of funding to ensure compliance with donor wishes.
- Grant revenue: Many non-profits rely heavily on grants. The P&L should track grant-related income and expenses separately.
- Fundraising efficiency: The cost of fundraising relative to the funds raised is a key metric for non-profits.
- In-kind donations: Non-cash contributions should be properly valued and included in the P&L statement.
VIII. Profit And Loss Statement for Small Businesses vs. Large Corporations
A. Key Differences
- Complexity and detail:
- Small businesses often have simpler P&L statements with fewer line items.
- Large corporations typically have more complex P&L statements with detailed breakdowns of revenue and expenses by division or product line.
- Frequency of reporting:
- Small businesses might prepare P&L statements monthly or quarterly for internal use.
- Large corporations often produce quarterly statements for public reporting and more frequent internal reports.
- Level of scrutiny:
- Small businesses’ P&L statements are typically reviewed internally or by a local accountant.
- Large corporations’ statements are often audited by major accounting firms and scrutinized by investors and analysts.
- Regulatory requirements:
- Small businesses generally have fewer regulatory reporting requirements.
- Large, publicly traded corporations must comply with SEC regulations and more stringent accounting standards.
B. Tailoring Profit And Loss Statement Practices to Business Size
- Small businesses:
- Focus on cash flow alongside profitability
- Emphasize break-even analysis
- Use P&L data for tax planning and loan applications
- Integrate P&L analysis with personal financial planning for owners
- Large corporations:
- Implement segment reporting for different business units or geographical regions
- Use consolidated statements to provide an overall view of complex organizational structures
- Employ sophisticated financial modeling and forecasting techniques
- Utilize P&L data for strategic planning and investor relations
- Adapting P&L structure as the business grows:
- Gradually increase the detail and complexity of P&L reporting
- Implement more advanced accounting software and practices
- Develop more comprehensive internal controls and review processes
- Align P&L reporting with industry standards and best practices
IX. Real-World Case Studies
A. How Successful Companies Use Profit And Loss Statement
- Amazon:
- Uses detailed P&L analysis to drive investment decisions in new business areas
- Leverages segment reporting to evaluate the performance of diverse business units (e.g., e-commerce, AWS, physical stores)
- Focuses on long-term growth over short-term profitability, as reflected in their P&L strategy
- Apple:
- Utilizes gross margin analysis to inform product strategy and pricing
- Uses P&L data to balance investment in R&D with maintaining industry-leading profit margins
- Leverages geographic segment reporting to guide global expansion strategies
- Walmart:
- Employs P&L insights to drive cost reduction initiatives across its vast operations
- Uses detailed category-level P&L analysis to optimize product mix and pricing
- Leverages P&L data to evaluate the performance of different store formats and e-commerce operations
B. Lessons Learned from P&L-Driven Turnarounds
- IBM’s shift to services and cloud computing:
- Used P&L analysis to identify declining profitability in hardware business
- Leveraged segment reporting to guide strategic shift towards higher-margin services and cloud offerings
- Demonstrated the importance of using P&L data to drive long-term strategic decisions
- Netflix’s transition from DVD rentals to streaming:
- Utilized P&L forecasting to predict the decline of the DVD rental market
- Used contribution margin analysis to guide investment in streaming content
- Showcased the value of using P&L data to anticipate and lead market transitions
- General Motors’ restructuring post-2008 financial crisis:
- Employed detailed P&L analysis to identify unprofitable brands and models
- Used contribution margin data to streamline product lines and reduce complexity
- Demonstrated how P&L-driven decision making can guide major organizational restructuring
X. Expert Insights and Tips
A. Interviews with CFOs and Financial Analysts
- Jane Doe, CFO of a Fortune 500 company:
“The key to effective P&L management is to look beyond the bottom line. We focus on trends in our operating margins and use this data to drive continuous improvement across all our business units.” - John Smith, Financial Analyst at a leading investment bank:
“When analyzing a company’s P&L, I always look for consistency in revenue growth and margin expansion. Erratic patterns often indicate underlying business challenges.” - Common pitfalls identified by experts:
- Over-reliance on a single profitability metric
- Failure to consider industry-specific factors in P&L analysis
- Neglecting to align P&L reporting with strategic objectives
B. Insider Tricks for Maximizing Profit And Loss Statement Utility
- Using sensitivity analysis for decision-making:
- Create multiple P&L scenarios based on different assumptions
- Use this analysis to understand the potential impact of major decisions or market changes
- Implementing rolling forecasts:
- Continuously update P&L forecasts based on the most recent data
- Use this approach to maintain a forward-looking view of financial performance
- Leveraging P&L data for performance-based compensation:
- Tie executive and employee bonuses to specific P&L metrics
- Ensure alignment between individual performance and overall financial goals
- Implementing driver-based P&L models:
- Identify key business drivers that impact P&L performance
- Create models that link these drivers to financial outcomes for more accurate forecasting
By understanding these industry-specific considerations, appreciating the differences between small and large business P&L practices, learning from real-world examples, and implementing expert advice, businesses can significantly enhance their use of profit and loss statements as a strategic tool for financial management and decision-making.
XI. Future Trends in Profit And Loss Statement Reporting
A. Impact of AI and Machine Learning
- Predictive analytics for forecasting:
- AI algorithms can analyze historical P&L data and external factors to generate more accurate revenue and expense forecasts.
- Machine learning models can continuously improve forecast accuracy by learning from past predictions and actual results.
- Automated anomaly detection and fraud prevention:
- AI-powered systems can scan P&L statements in real-time to identify unusual patterns or discrepancies.
- These systems can alert financial teams to potential errors or fraudulent activities, enhancing the integrity of financial reporting.
- Natural language processing for narrative financial reports:
- AI can generate human-readable narratives explaining P&L trends and insights.
- This technology can help make financial reports more accessible to non-financial stakeholders.
B. Evolving Regulatory Landscape
- Changes in accounting standards:
- Ongoing convergence efforts between IFRS and GAAP may impact P&L reporting practices.
- Increased focus on principles-based standards may require more judgment in P&L preparation and analysis.
- Increased focus on non-financial metrics:
- Growing emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting may lead to the integration of sustainability metrics in P&L statements.
- Regulators may require more disclosure on human capital, customer satisfaction, and other non-financial performance indicators.
- Growing demand for real-time financial data:
- Regulatory bodies may push for more frequent or even continuous financial reporting.
- This could lead to a shift from periodic P&L statements to real-time financial dashboards.
C. Predictions for the Future of Financial Reporting
- Integration of financial and operational data:
- P&L statements may evolve to include more operational metrics, providing a holistic view of business performance.
- This integration could lead to more sophisticated performance analysis and decision-making tools.
- Shift towards continuous, real-time reporting:
- Traditional periodic P&L statements may be replaced by continuously updated financial data streams.
- This could enable more agile decision-making and responsive business strategies.
- Increased transparency and stakeholder engagement:
- Future P&L reporting may include interactive elements allowing stakeholders to drill down into specific areas of interest.
- This could lead to more collaborative financial planning and analysis processes involving a wider range of stakeholders.
XII. Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Points
- The critical role of P&L statements in business success:
- P&L statements are essential tools for assessing financial health, guiding decision-making, and attracting investors.
- Mastering P&L analysis can provide a significant competitive advantage in today’s business landscape.
- Importance of accurate creation and analysis:
- Following best practices in P&L preparation ensures the reliability of financial data.
- Advanced analysis techniques like ratio analysis and trend forecasting unlock deeper insights from P&L statements.
- Value of leveraging technology and advanced techniques:
- Modern software solutions streamline P&L creation and analysis processes.
- Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning are set to revolutionize financial reporting and analysis.
B. Call to Action for Implementing P&L Best Practices
- Review and improve P&L processes:
- Assess your current P&L practices against the best practices outlined in this guide.
- Identify areas for improvement and develop an action plan to enhance your P&L reporting and analysis capabilities.
- Embrace technological advancements:
- Explore how modern accounting software and analytics tools can enhance your P&L management.
- Stay informed about emerging technologies and consider how they might be applied to your financial reporting processes.
- Foster a culture of financial literacy:
- Encourage non-financial managers to engage with P&L data and insights.
- Provide training and resources to help all stakeholders understand and utilize P&L information effectively.
- Align P&L practices with strategic goals:
- Ensure that your P&L reporting and analysis support your overall business strategy.
- Use P&L insights to drive continuous improvement and inform long-term planning.
In conclusion, mastering profit and loss statements is more than just a financial exercise—it’s a crucial step towards achieving business excellence. By implementing the techniques, insights, and best practices shared in this comprehensive guide, businesses of all sizes and across all industries can transform their approach to financial management.
As we’ve explored, P&L statements are powerful tools for assessing financial health, guiding strategic decisions, and driving business growth. From understanding the basics of P&L creation to leveraging advanced analysis techniques and emerging technologies, there are numerous ways to enhance the value derived from these essential financial documents.
The business landscape is continually evolving, with new challenges and opportunities emerging regularly. Those who can effectively create, analyze, and act upon their P&L statements will be best positioned to navigate this dynamic environment and achieve sustainable success.
Remember, the journey to financial mastery is ongoing. As you implement these strategies and best practices, continue to learn, adapt, and refine your approach. By doing so, you’ll not only improve your financial reporting but also enhance your overall business performance, positioning your organization for long-term success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
You can Learn more at Forbes.com


Leave a Reply